Knowing which IRS forms to use and when is just one of the many challenges people face with their federal taxes.
It’s for this reason that many people turn to professionals. But in order to do even that… you guessed it… you need to file an IRS tax form.
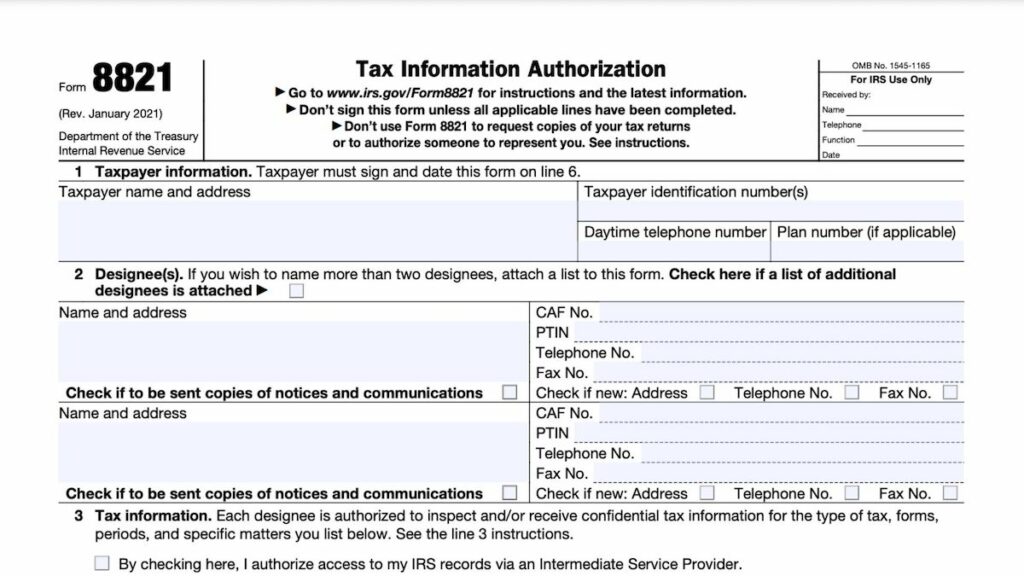
IRS Form 8821 grants authorization for the IRS to share your tax information with an appointed person or company. So if, for example, you’re looking for help filing or reviewing your taxes, you’ll need Form 8821.
However, if you’re looking for someone who can also represent you before the IRS and negotiate on your behalf, you’ll need Form 2848, which grants IRS power of attorney; Form 8821 isn’t enough.
It’s important to understand the differences between IRS Forms 8221 and 2848, and exactly what you are authorizing by filing each of these forms. So, if you’re looking to appoint a third party to help with your taxes in any way at all, keep reading to ensure you understand the form you need.
What is IRS Form 8821?
The IRS is bound by law to keep your tax information confidential.
This means that if you want or need any third party to be able to see any of your tax information, you need to grant authorization by filing Form 8821.
IRS Form 8821 allows you to:
- Authorize any individual or company (including friends, family, and non-tax professionals) to access your confidential tax information
- Specify the exact type of tax, tax matters, and years or periods that they can access
- Choose whether the same contact receives copies of all new IRS notices
- Delete or revoke prior tax information authorizations
Once filed, your authorized contact will have access to the specified tax information for the designated period. If none is specified and it’s not revoked beforehand, the authorization automatically expires after 7 years.
However, it’s important to note that Form 8821 does NOT authorize your designee the right to represent you before the IRS. This is the main difference between Form 8821 and 2848, which we’ll explain below.
When to file Form 8821
There are several circumstances when you might want or need to grant permission for someone to review your tax information, but not represent you.
These include:
- Appointing tax professionals to give you tax advice and/or file your tax returns
- Requesting assistance or advice on your taxes from another person or professional
- Providing income verification, e.g. if applying for a mortgage
If you need more substantial help with your taxes, such as negotiating tax relief settlements or other forms of representation with the IRS, you will need to file Form 2848 instead.
What is the difference between IRS Form 8821 and 2848?
Form 8821 is for Tax Information Authorization only.
Form 2848 is for IRS Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative.
These are often confused as they both grant third-party access to your confidential tax information. However, the ability – or lack thereof – to represent you before the IRS is a significant one.
The designee of Form 8821 is only granted the ability to inspect and receive your tax information. They are NOT authorized to:
- speak on your behalf
- request the disclosure of your information to another third party
- advocate your position regarding federal tax laws
- execute waivers, consents, or closing agreements
- represent you in any other manner before the IRS
If you want your appointee to be able to do any of these things – including, for example, negotiating a payment plan for back taxes, appealing a dispute, seeking tax penalty abatement, or responding to notices on your behalf, you would need to file Form 2848, IRS Power of Attorney.
The other main differences between Forms 8821 and 2848 are:
- The appointee on Form 2848 must be eligible to practice before the IRS (e.g. an Enrolled Agent, CPA, or other specific type of tax professional)
- The power of attorney must be explicitly revoked, it doesn’t automatically expire after the designated period
How to file Form 8821 and 2848
Both Forms 8821 and 2848 can be filed online, by fax, or in paper by mail:
If you’re enlisting professionals to help you resolve your tax debt, and therefore need to file a Form 2848 to grant them power of attorney, the professionals in question will also be able to help you file this form – taking yet another thing off your plate.
Enlisting professional help to manage your federal tax debt
Tax debt is a highly complex subject. So just as hiring a lawyer will always be your best course of action if you need legal advice and representation in a court of law; hiring professional tax experts is your best course of action if you need tax relief advice and representation in front of the IRS.
Here at Tax Relief Helpers we are on a mission to help our clients combat the threats of the IRS and save millions of dollars in tax debt every year. So if you have tax debt or other concerns that you need to handle with the IRS, contact us today for a completely free consultation and find out exactly how we can help you.
The very first thing we do with new clients is file Form 2848 to establish power of attorney – so that we can examine everything that the IRS knows about you, give you the best advice, build your optimal tax case, and then handle everything with the IRS directly, on your behalf.